You likely don’t notice it on a daily basis, but your vision is divided into several different sections that span a 170-degree field. The view when you stare straight ahead is called the central field. Everything that lies outside of the central gaze is known as peripheral vision. But even that is divided into three segments, which include:
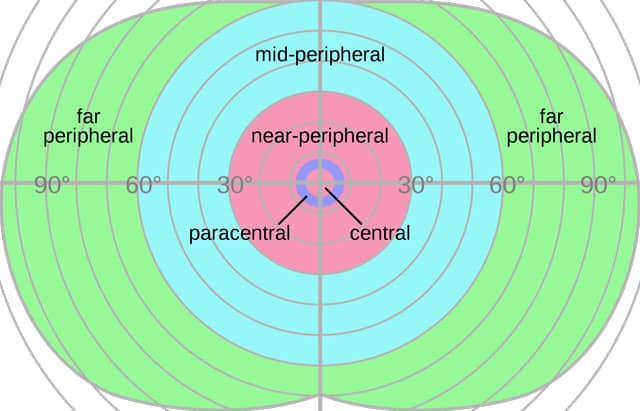
- Near-Peripheral Vision: The vision field closest to the center gaze
- Mid-Peripheral Vision: The vision in the middle field of view
- Far-Peripheral Vision: The vision at the very edge of view without turning your head
Peripheral vision loss, or PVL, causes a condition that is sometimes referred to as tunnel vision. A person experiencing PVL can’t see outside of their central field without turning their head.
Causes of PVL
In most cases, peripheral vision loss is linked to nerve damage. Other causes include:
- Compressed optic nerve head
- Concussion
- Eye strokes
- Brain damage
- Injury
- Stroke
- Detached retina
- Optic neuritis or other types of neurological damage
If you’re concerned about losing peripheral vision, see an eye doctor immediately. Some simple field tests can determine the extent of your PVL and allow your doctor to begin planning treatment that could save your vision or even your life.
Symptoms of Peripheral Vision Loss
When it’s not caused by stroke or injury, symptoms of PVL can be so subtle you don’t even notice them until the loss is significant. The symptoms can also depend on what’s causing the PVL. For example, PVL brought on by glaucoma affects the edges of vision first, while PVL related to scotoma may first present as a blind spot in your peripheral vision.
For those who have not yet been diagnosed with vision-related disorders, general warning symptoms of PVL include:
- Trouble seeing in the dark
- Trouble with vision while driving
- Falling/tripping
- Bumping into walls or other stationary objects
- Difficulty navigating through big crowds
Because PVL can be a sign of a serious health problem, it’s important to discuss any vision concerns with your doctor as soon as possible. Also consider that it may be unsafe for you to drive or participate in other high-risk activities if you have peripheral vision loss.
Treatment for Peripheral Vision Loss
Treatments for PVL vary depending on the underlying cause. For example, if your vision loss is caused by diabetic retinopathy, controlling high blood pressure and blood sugar levels may slow and even improve the PVL. Your doctor will recommend the correct treatment for your condition.
Some research suggests prism glasses can help improve certain types of PVL.
While there is little to no research supporting the use of natural remedies to improve peripheral vision, many of the suggestions are safe and good for general health. Do not use these or any other suggestions as an alternative to medical advice. Always consult your doctor about vision concerns and follow his or her course of treatment.
Natural Treatments
There are a number of natural options that can be explored for PVL. These include:
- Practicing Yogic eye exercises
- Eating a diet rich in carrots, sweet potatoes, blueberries, beets, fatty fish, and leafy greens
- Avoiding eye strain
- Drinking cucumber juice
- Acupressure or acupuncture
Unfortunately, for many people, peripheral vision loss can’t be restored. The best treatment is to address vision problems with your doctor as soon as you notice them. Finding and treating the cause of PVL is the best hope for improving peripheral vision or at least slowing its progression.
Sources
- Featured Image, Zyxwv99, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons

Leave a Reply